The classification of mixtures for acute hazards based on this summation of the concentrations of
classified ingredients is summarized in Table 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.2.2 below.
Table 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.2.2: Classification of a mixture for acute hazards based on summation of the concentrations
of classified ingredients
|
Sum of the concentrations (in %) of ingredients
classified as:
|
Mixture classified as: |
| Acute 1 × M a ≥ 25% | Acute 1 |
a For explanation of the M factor, see 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.4.
Classification for categories Chronic 1 and 2
First, all ingredients classified as Chronic 1 are considered. If the sum of the concentrations (in %)
of these ingredients is greater than or equal to 25% the mixture shall be classified as Chronic 1. If
the result of the calculation is a classification of the mixture as Chronic 1 the classification
procedure is completed.
In cases where the mixture is not classified as Chronic 1, classification of the mixture as Chronic 2
is considered. A mixture shall be classified as Chronic 2 if 10 times the sum of the concentrations
(in %) of all ingredients classified as Chronic 1 plus the sum of the concentrations (in %) of all
ingredients classified as Chronic 2 is greater than or equal to 25%. If the result of the calculation is
classification of the mixture as Chronic 2, the classification process is completed.
The classification of mixtures for long-term hazards based on this summation of the concentrations
of classified ingredients is summarized in Table 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.3.3 below.
Table 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.3.3: Classification of a mixture for long-term hazards based on summation of the
concentrations of classified ingredients
|
Sum of the concentrations (in %) of ingredients
classified as:
|
Mixture classified as: |
| Chronic 1 × M a ≥ 25% | Chronic 1 |
| (M × 10 × Chronic 1) + Chronic 2 ≥ 25% | Chronic 2 |
a For explanation of the M factor, see 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.4.
Mixtures with highly toxic ingredients
Acute 1 or Chronic 1 ingredients with acute toxicities well below 1 mg/l and/or chronic toxicities
well below 0.1 mg/l (if non-rapidly degradable) and 0.01 mg/l (if rapidly degradable) may
influence the toxicity of the mixture and are given increased weight in applying the summation
method. When a mixture contains ingredients classified as acute or Chronic 1, the tiered approach
described in 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.2 and 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.3 shall be applied using a weighted sum by
multiplying the concentrations of Acute 1 and Chronic 1 ingredients by a factor, instead of merely
adding up the percentages. This means that the concentration of "Acute 1" in the left column of
Table 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.2.2 and the concentration of "Chronic 1" in the left column of Table
2.2.9.1.10.4.6.3.3 are multiplied by the appropriate multiplying factor. The multiplying factors to
be applied to these ingredients are defined using the toxicity value, as summarised in
Table 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.4 below. Therefore, in order to classify a mixture containing Acute 1 and/or
Chronic 1 ingredients, the classifier needs to be informed of the value of the M factor in order to
apply the summation method. Alternatively, the additivity formula (see 2.2.9.1.10.4.5.2) may be
used when toxicity data are available for all highly toxic ingredients in the mixture and there is
convincing evidence that all other ingredients, including those for which specific acute and/or
chronic toxicity data are not available, are of low or no toxicity and do not significantly contribute
to the environmental hazard of the mixture.
Table 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.4: Multiplying factors for highly toxic ingredients of mixtures
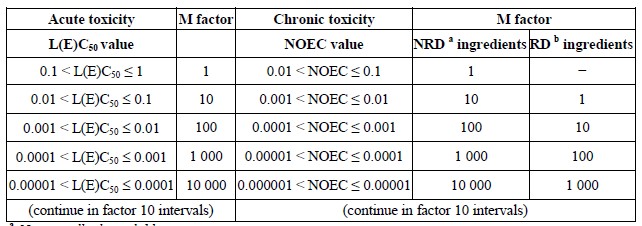
a Non-rapidly degradable.
b Rapidly degradable.
Classification of mixtures with ingredients without any useable information
In the event that no useable information on acute and/or chronic aquatic toxicity is available for one or
more relevant ingredients, it is concluded that the mixture cannot be attributed (a) definitive hazard
category(ies). In this situation the mixture shall be classified based on the known ingredients only
with the additional statement that: "x percent of the mixture consists of ingredient(s) of unknown
hazard to the aquatic environment.
Substances or mixtures classified as environmentally hazardous substances (aquatic environment) on
the basis of Regulation 1272/2008/EC3
If data for classification according to the criteria of 2.2.9.1.10.3 and 2.2.9.1.10.4 are not available, a
substance or mixture:
(a) Shall be classified as an environmentally hazardous substance (aquatic environment) if it has to
be assigned category(ies) Aquatic Acute 1, Aquatic Chronic 1 or Aquatic Chronic 2 according
to Regulation 1272/2008/EC3;
(b) May be regarded as not being an environmentally hazardous substance (aquatic environment)
if it does not have to be assigned such a category according to the said Regulation.
Assignment of substances or mixtures classified as environmentally hazardous substances (aquatic
environment) according to the provisions in 2.2.9.1.10.3, 2.2.9.1.10.4 or 2.2.9.1.10.5
Substances or mixtures classified as environmentally hazardous substances (aquatic environment), not
otherwise classified under ADR shall be designated:
UN No. 3077 ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, SOLID, N.O.S.; or
UN No. 3082 ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, LIQUID, N.O.S.
They shall be assigned to packing group III.
Genetically modified microorganisms or organisms
Genetically modified microorganisms (GMMOs) and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are
microorganisms and organisms in which genetic material has been purposely altered through genetic
engineering in a way that does not occur naturally. They are assigned to Class 9 (UN No. 3245) if they
do not meet the definition of toxic substances or of infectious substances, but are capable of altering
animals, plants or microbiological substances in a way not normally the result of natural reproduction.
NOTE 1: GMMOs and GMOs which are infectious are substances of Class 6.2, UN Nos. 2814,
2900 or 3373.
NOTE 2: GMMOs or GMOs are not subject to the provisions of ADR when authorized for use by
the competent authorities of the countries of origin, transit and destination14.
NOTE 3: Genetically modified live animals which, in accordance with the current state of scientific
knowledge, have no known pathogenic effect on humans, animals and plants and are carried in
receptacles that are suitable for safely preventing both the escape of the animals and unauthorized
access to them, are not subject to the provisions of ADR. The provisions specified by the International
Air Transport Association (IATA) for air transport “Live Animals Regulations, LAR” can be drawn
on as guidelines for suitable receptacles for the transport of live animals.
NOTE 4: Live animals shall not be used to carry genetically modified microorganisms classified in
Class 9 unless the substance can be carried no other way. Genetically modified live animals shall be
carried under terms and conditions of the competent authorities of the countries of origin and
destination.
3 Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on
classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directive 67/548/EEC and
1999/45/EC; and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006, published in the Official Journal of the European Union,
L 353, 31 December 2008, p 1-1355.
14 See Part C of Directive 2001/18/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the deliberate release
into the environment of genetically modified organisms and repealing Council Directive 90/220/EEC (Official Journal
of the European Communities, No. L 106, of 17 April 2001, pp 8-14) and Regulation (EC) No. 1829/2003 of the
European Parliament and of the Council on genetically modified food and feed (Official Journal of the European
Union, No. L 268, of 18 October 2003, pp 1-23), which set out the authorization procedures for the European Union.
(Deleted)
Elevated temperature substances
Elevated temperature substances include substances which are carried or handed over for carriage in
the liquid state at or above 100 °C and, in the case of those with a flash-point, below their flash-point.
They also include solids which are carried or handed over for carriage at or above 240 °C.
NOTE: Elevated temperature substances may be assigned to Class 9 only if they do not meet the
criteria of any other class.
Other substances presenting a danger during carriage but not meeting the definitions of another
class.
The following other miscellaneous substances not meeting the definitions of another class are
assigned to Class 9:
Solid ammonia compounds having a flash-point below 60 °C;
Low hazard dithionites;
Highly volatile liquids;
Substances emitting noxious fumes;
Substances containing allergens;
Chemical kits and first aid kits;
Electric double layer capacitors (with an energy storage capacity greater than 0.3 Wh);
Vehicles, engines and machinery, internal combustion.
NOTE: UN No. 1845 carbon dioxide, solid (dry ice)15, UN No. 2071 ammonium nitrate fertilizers, UN
No. 2216 fish meal (fish scrap), stabilized, UN No. 2807 magnetized material, UN No. 3334 aviation
regulated liquid, n.o.s., UN No. 3335 aviation regulated solid, n.o.s. and UN No. 3363 dangerous
goods in machinery or dangerous goods in apparatus listed in the UN Model Regulations, are not
subject to the provisions of ADR.
Assignment of the packing groups
When indicated in column (4) of Table A of Chapter 3.2, substances and articles of Class 9 are
assigned to one of the following packing groups according to their degree of danger:
Packing group II: substances presenting medium danger;
Packing group III: substances presenting low danger.
Substances and articles not accepted for carriage
The following substances and articles shall not be accepted for carriage:
- Lithium batteries which do not meet the relevant conditions of special provisions 188, 230, 310
or 636 of Chapter 3.3;
- Uncleaned empty containment vessels for apparatus such as transformers, condensers and
hydraulic apparatus containing substances assigned to UN Nos. 2315, 3151, 3152 or 3432.
15 For
15 For UN No. 1845 carbon dioxide, solid (dry ice) used as a coolant, see 5.5.3.
