(Reserved)
(Reserved)
Designatory code system for IBCs
|
Type |
|||
|
under press than 10 kPa (0.1 bar) |
r liquids |
||
|
Rigid |
11 |
21 |
31 |
|
Flexible |
13 |
- |
- |
The following types and codes of IBC are assigned:
|
Material |
Category |
Code |
Sub- section |
|
Metal |
|||
|
11A |
|||
|
for solids, filled or discharged under pressure |
21A |
||
|
for liquids |
31A |
||
|
B. Aluminium |
for solids, filled or discharged by gravity |
11B |
|
|
for solids, filled or discharged under pressure |
21B |
6.5.5.1 |
|
|
for liquids |
31B |
||
|
N. Other than steel or aluminium |
for solids, filled or discharged by gravity |
11N |
|
|
for solids, filled or discharged under pressure |
21N |
||
|
for liquids |
31N |
||
|
Flexible |
|||
|
H. Plastics |
woven plastics without coating or liner |
13H1 |
|
|
woven plastics, coated |
13H2 |
||
|
woven plastics with liner |
13H3 |
||
|
woven plastics, coated and with liner |
13H4 |
||
|
plastics film |
13H5 |
||
|
L. Textile |
without coating or liner |
13L1 |
6.5.5.2 |
|
coated |
13L2 |
||
|
with liner |
13L3 |
||
|
coated and with liner |
13L4 |
||
|
M. Paper |
multiwall |
13M1 |
|
|
multiwall, water resistant |
13M2 |
||
|
H. Rigid plastics |
for solids, filled or discharged by gravity, fitted with |
11H1 |
|
|
s, filled or discharged by gravity, freestanding |
11H2 |
||
|
for solids, filled or discharged under pressure, fitted with structural equipment |
21H1 |
6.5.5.3 |
|
|
for solids, filled or discharged under pressure, freestanding |
21H2 |
||
|
for liquids, fitted with structural equipment |
31H1 |
||
|
for liquids, freestanding |
31H2 |
|
Material |
Category |
Code |
Sub- section |
|
HZ. Composite tics inner |
for solids, filled or discharged by gravity, with rigid plastics inner receptacle |
11HZ1 |
6.5.5.4 |
|
with flexible |
11HZ2 |
||
|
for solids, filled or discharged under pressure, with rigid plastics inner receptacle |
21HZ1 |
||
|
for solids, filled or discharged under pressure, with flexible plastics inner receptacle |
21HZ2 |
||
|
for liquids, with rigid plastics inner receptacle |
31HZ1 |
||
|
for liquids, with flexible plastics inner receptacle |
31HZ2 |
||
|
G. Fibreboard |
for solids, filled or discharged by gravity |
11G |
6.5.5.5 |
|
Wooden |
|||
|
C. Natural wood |
for solids, filled or discharged by gravity with inner liner |
11C |
6.5.5.6 |
|
D. Plywood |
for solids, filled or discharged by gravity, with inner liner |
11D |
|
|
F. Reconstituted wood |
for solids, filled or discharged by gravity, with inner liner |
11F |
|
Marking
Primary marking
 ;
;
Examples of marking for various types of IBC in accordance with 6.5.2.1.1 (a) to (h) above:

Additional marking
Each IBC shall bear the marks required in 6.5.2.1 and, in addition, the following information which
may appear on a corrosion-resistant plate permanently attached in a place readily accessible for inspection:
|
Additional marks |
Category of IBC |
||||
|
Metal |
Rigid plastics |
Composite |
Fibreboard |
Wooden |
|
|
Capacity in litres a at 20 °C |
X |
X |
X |
||
|
Tare mass in kg a |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
Test (gauge) pressure, in kPa or bar a, if applicable |
X |
X |
|||
|
Maximum filling / discharge pressure in kPa or bar a , if applicable |
X |
X |
X |
||
|
Body material and its minimum thickness in mm |
X |
||||
|
Date of last leakproofness test, if applicable (month and year) |
X |
X |
X |
||
|
Date of last inspection (month and year) |
X |
X |
X |
||
|
Serial number of the manufacturer |
X |
||||
|
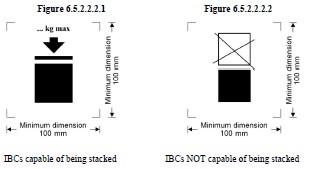
Maximum permitted stacking load b |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
a The unit used shall be indicated.
b See 6.5.2.2.2. This additional mark shall apply to all IBCs manufactured, repaired or remanufactured as from 1 January 2011 (see also 1.6.1.15).