2.5 year periodic inspection and test as required by 6.7.2.19.2. However, a portable tank filled prior to
the date of expiry of the last periodic inspection and test may be carried for a period not to exceed
three months beyond the date of expiry of the last periodic test or inspection. In addition, a portable
tank may be carried after the date of expiry of the last periodic test and inspection:
(a) After emptying but before cleaning, for purposes of performing the next required test or
inspection prior to refilling; and
(b) Unless otherwise approved by the competent authority, for a period not to exceed six months
beyond the date of expiry of the last periodic test or inspection, in order to allow the return of
dangerous goods for proper disposal or recycling. Reference to this exemption shall be
mentioned in the transport document.
The exceptional inspection and test is necessary when the portable tank shows evidence of damaged
or corroded areas, or leakage, or other conditions that indicate a deficiency that could affect the
integrity of the portable tank. The extent of the exceptional inspection and test shall depend on the
amount of damage or deterioration of the portable tank. It shall include at least the 2.5 year inspection
and test according to 6.7.2.19.5.
The internal and external examinations shall ensure that:
(a) The shell is inspected for pitting, corrosion, or abrasions, dents, distortions, defects in welds or
any other conditions, including leakage, that might render the portable tank unsafe for carriage.
The wall thickness shall be verified by appropriate measurement if this inspection indicates a
reduction of wall thickness;
(b) The piping, valves, heating/cooling system, and gaskets are inspected for corroded areas,
defects, or any other conditions, including leakage, that might render the portable tank unsafe
for filling, discharge or carriage;
(c) Devices for tightening manhole covers are operative and there is no leakage at manhole covers
or gaskets;
(d) Missing or loose bolts or nuts on any flanged connection or blank flange are replaced or
tightened;
(e) All emergency devices and valves are free from corrosion, distortion and any damage or defect
that could prevent their normal operation. Remote closure devices and self-closing stop-valves
shall be operated to demonstrate proper operation;
(f) Linings, if any, are inspected in accordance with criteria outlined by the lining manufacturer;
(g) Required marks on the portable tank are legible and in accordance with the applicable
requirements; and
(h) The framework, supports and arrangements for lifting the portable tank are in a satisfactory
condition.
The inspections and tests in 6.7.2.19.1, 6.7.2.19.3, 6.7.2.19.4, 6.7.2.19.5 and 6.7.2.19.7 shall be
performed or witnessed by an expert approved by the competent authority or its authorized body.
When the pressure test is a part of the inspection and test, the test pressure shall be the one indicated
on the data plate of the portable tank. While under pressure, the portable tank shall be inspected for
any leaks in the shell, piping or equipment.
In all cases when cutting, burning or welding operations on the shell have been effected, that work
shall be to the approval of the competent authority or its authorized body taking into account the
pressure vessel code used for the construction of the shell. A pressure test to the original test pressure
shall be performed after the work is completed.
When evidence of any unsafe condition is discovered, the portable tank shall not be returned to
service until it has been corrected and the test is repeated and passed. .
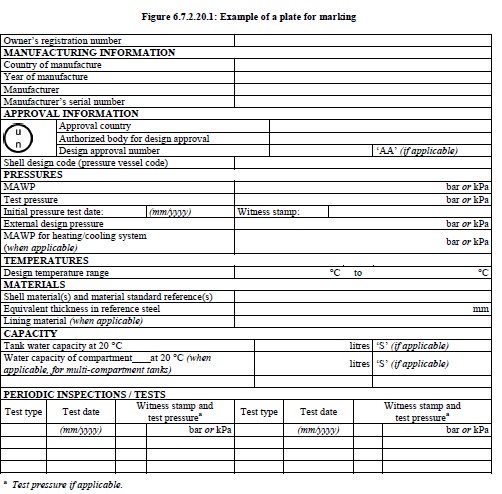
Marking
Every portable tank shall be fitted with a corrosion resistant metal plate permanently attached to the
portable tank in a conspicuous place readily accessible for inspection. When for reasons of portable
tank arrangements the plate cannot be permanently attached to the shell, the shell shall be marked with
at least the information required by the pressure vessel code. As a minimum, at least the following
information shall be marked on the plate by stamping or by any other similar method:
(a) Owner information
(i) Owner’s registration number;
(b) Manufacturing information
(i) Country of manufacture;
(ii) Year of manufacture;
(iii) Manufacturer’s name or mark;
(iv) Manufacturer’s serial number;
(c) Approval information
(i) The United Nations packaging symbol 

;
This symbol shall not be used for any purpose other than certifying that a packaging, a
flexible bulk container, a portable tank or a MEGC complies with the relevant
requirements in Chapter 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.5, 6.6, 6.7 or 6.11;
(ii) Approval country;
(iii) Authorized body for the design approval;
(iv) Design approval number;
(v) Letters ‘AA’, if the design was approved under alternative arrangements (see 6.7.1.2);
(vi) Pressure vessel code to which the shell is designed;
(d) Pressures
(i) MAWP (in bar gauge or kPa gauge)3;
(ii) Test pressure (in bar gauge or kPa gauge)3;
(iii) Initial pressure test date (month and year);
(iv) Identification mark of the initial pressure test witness;
(v) External design pressure4 (in bar gauge or kPa gauge)3;
(vi) MAWP for heating/cooling system (in bar gauge or kPa gauge)3 (when applicable);
(e) Temperatures
(i) Design temperature range (in °C)3;
3 The unit used shall be indicated.
4 See 6.7.2.2.10.
(f) Materials
(i) Shell material(s) and material standard reference(s);
(ii) Equivalent thickness in reference steel (in mm)3;
(iii) Lining material (when applicable);
(g) Capacity
(i) Tank water capacity at 20 °C (in litres)3;
This indication is to be followed by the symbol "S" when the shell is divided by surge
plates into sections of not more than 7 500 litres capacity;
(ii) Water capacity of each compartment at 20 °C (in litres)3 (when applicable, for multicompartment
tanks).
This indication is to be followed by the symbol "S" when the compartment is divided by
surge plates into sections of not more than 7 500 litres capacity;
(h) Periodic inspections and tests
(i) Type of the most recent periodic test (2.5-year, 5-year or exceptional);
(ii) Date of the most recent periodic test (month and year);
(iii) Test pressure (in bar gauge or kPa gauge)3 of the most recent periodic test (if
applicable);
(iv) Identification mark of the authorized body who performed or witnessed the most recent
test.
3 The unit used shall be indicated.
The following particulars shall be durably marked either on the portable tank itself or on a metal plate
firmly secured to the portable tank:
Name of the operator
Maximum permissible gross mass (MPGM) ___________ kg
Unladen (tare) mass ___________ kg
Portable tank instruction in accordance with 4.2.5.2.6
NOTE: For the identification of the substances being carried, see also Part 5.
If a portable tank is designed and approved for handling in open seas, the words "OFFSHORE
PORTABLE TANK" shall be marked on the identification plate.
Requirements for the design, construction, inspection and testing of portable tanks intended for the carriage of non-refrigerated liquefied gases
NOTE: These requirements also apply to portable tanks intended for the carriage of chemicals under
pressure (UN Nos. 3500, 3501, 3502, 3503, 3504 and 3505).
Definitions
For the purposes of this section:
Alternative arrangement means an approval granted by the competent authority for a portable tank or
MEGC that has been designed, constructed or tested to technical requirements or testing methods
other than those specified in this Chapter;
Portable tank means a multimodal tank having a capacity of more than 450 litres used for the carriage
of non-refrigerated liquefied gases of Class 2. The portable tank includes a shell fitted with service
equipment and structural equipment necessary for the carriage of gases. The portable tank shall be
capable of being filled and discharged without the removal of its structural equipment. It shall possess
stabilizing members external to the shell, and shall be capable of being lifted when full. It shall be
designed primarily to be loaded onto a vehicle, wagon or sea-going or inland navigation vessel and
shall be equipped with skids, mountings or accessories to facilitate mechanical handling. Tankvehicles,
tank-wagons, non-metallic tanks, intermediate bulk containers (IBCs), gas cylinders and
large receptacles are not considered to fall within the definition for portable tanks;
Shell means the part of the portable tank which retains the non-refrigerated liquefied gas intended for
carriage (tank proper), including openings and their closures, but does not include service equipment
or external structural equipment;
Service equipment means measuring instruments and filling, discharge, venting, safety and insulating
devices;
Structural equipment means the reinforcing, fastening, protective and stabilizing members external to
the shell;
Maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) means a pressure that shall be not less than the
highest of the following pressures measured at the top of the shell while in operating position, but in
no case less than 7 bar:
(a) The maximum effective gauge pressure allowed in the shell during filling or discharge; or
(b) The maximum effective gauge pressure to which the shell is designed, which shall be:
(i) for a non-refrigerated liquefied gas listed in the portable tank instruction T50
in 4.2.5.2.6, the MAWP (in bar) given in T50 portable tank instruction for that gas;
(ii) for other non-refrigerated liquefied gases, not less than the sum of:
- the absolute vapour pressure (in bar) of the non-refrigerated liquefied gas at the
design reference temperature minus 1 bar; and
- the partial pressure (in bar) of air or other gases in the ullage space
being determined by the design reference temperature and the liquid phase
expansion due to an increase of the mean bulk temperature of tr -tf (tf = filling
temperature, usually 15 °C, tr = maximum mean bulk temperature, 50 °C);
(iii) for chemicals under pressure, the MAWP (in bar) given in T50 portable tank instruction
for the liquefied gas portion of the propellants listed in T50 in 4.2.5.2.6;
Design pressure means the pressure to be used in calculations required by a recognized pressure
vessel code. The design pressure shall be not less than the highest of the following pressures:
(a) The maximum effective gauge pressure allowed in the shell during filling or discharge; or
(b) The sum of:
(i) the maximum effective gauge pressure to which the shell is designed as defined in (b) of
the MAWP definition (see above); and
(ii) a head pressure determined on the basis of the static forces specified in 6.7.3.2.9, but not
less than 0.35 bar;
Test pressure means the maximum gauge pressure at the top of the shell during the pressure test;
Leakproofness test means a test using gas subjecting the shell and its service equipment to an effective
internal pressure of not less than 25% of the MAWP;
Maximum permissible gross mass (MPGM) means the sum of the tare mass of the portable tank and
the heaviest load authorized for carriage;
Reference steel means a steel with a tensile strength of 370 N/mm2 and an elongation at fracture
of 27%;
Mild steel means a steel with a guaranteed minimum tensile strength of 360 N/mm2 to 440 N/mm2 and
a guaranteed minimum elongation at fracture conforming to 6.7.3.3.3.3;
Design temperature range for the shell shall be -40 °C to 50 °C for non-refrigerated liquefied gases
carried under ambient conditions. More severe design temperatures shall be considered for portable
tanks subjected to severe climatic conditions;
Design reference temperature means the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the contents is
determined for the purpose of calculating the MAWP. The design reference temperature shall be less
than the critical temperature of the non-refrigerated liquefied gas or liquefied gas propellants of
chemicals under pressure intended to be carried to ensure that the gas at all times is liquefied. This
value for each portable tank type is as follows:
(a) Shell with a diameter of 1.5 metres or less: 65 °C;
(b) Shell with a diameter of more than 1.5 metres:
(i) without insulation or sun shield: 60 °C;
(ii) with sun shield (see 6.7.3.2.12): 55 °C; and
(iii) with insulation (see 6.7.3.2.12) : 50 °C;
Filling density means the average mass of non-refrigerated liquefied gas per litre of shell capacity
(kg/l). The filling density is given in portable tank instruction T50 in 4.2.5.2.6.
General design and construction requirements
Shells shall be designed and constructed in accordance with the requirements of a pressure vessel code
recognized by the competent authority. Shells shall be made of steel suitable for forming. The
materials shall in principle conform to national or international material standards. For welded shells,
only a material whose weldability has been fully demonstrated shall be used. Welds shall be skilfully
made and afford complete safety. When the manufacturing process or the materials make it necessary,
the shells shall be suitability heat-treated to guarantee adequate toughness in the weld and in the heat
affected zones. In choosing the material the design temperature range shall be taken into account with
respect to risk of brittle fracture, to stress corrosion cracking and to resistance to impact. When fine
grain steel is used, the guaranteed value of the yield strength shall be not more than 460 N/mm2 and
the guaranteed value of the upper limit of the tensile strength shall be not more than 725 N/mm2
according to the material specification. Portable tank materials shall be suitable for the external
environment in which they may be carried.
Portable tank shells, fittings and pipework shall be constructed of materials which are:
(a) Substantially immune to attack by the non-refrigerated liquefied gas(es) intended to be
carried; or
(b) Properly passivated or neutralized by chemical reaction.
