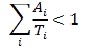Definition of high consequence dangerous goods
High consequence dangerous goods are those which have the potential for misuse in a terrorist event
and which may, as a result, produce serious consequences such as mass casualties, mass destruction
or, particularly for Class 7, mass socio-economic disruption.
High consequence dangerous goods in classes other than Class 7 are those listed in Table 1.10.3.1.2
below and carried in quantities greater than those indicated therein.
Table 1.10.3.1.2: List of high consequence dangerous goods
|
Class
|
Division
|
Substance or article
|
Quantity
|
|
Tank
(l) c
|
Bulk (kg) d
|
Packages (kg)
|
|
1
|
1.1
|
Explosives
|
a
|
a
|
0
|
|
1.2
|
Explosives
|
a
|
a
|
0
|
|
1.3
|
Compatibility group C explosives
|
a
|
a
|
0
|
|
1.4
|
Explosives of UN Nos. 0104, 0237, 0255, 0267, 0289,
0361, 0365, 0366, 0440, 0441, 0455, 0456 and 0500
|
a
|
a
|
0
|
|
1.5
|
Explosives
|
0
|
a
|
0
|
|
2
|
|
Flammable gases (classification codes including only the letter F)
|
3000
|
a
|
b
|
|
Toxic gases (classification codes including letters T, TF, TC, TO, TFC or TOC) excluding aerosols
|
0
|
a
|
0
|
|
3
|
|
Flammable liquids of packing groups I and II
|
3000
|
a
|
b
|
|
Desensitized explosives
|
0
|
a
|
0
|
|
4.1
|
|
Desensitized explosives
|
a
|
a
|
0
|
|
4.2
|
|
Packing group I substances
|
3000
|
a
|
b
|
|
4.3
|
|
Packing group I substances
|
3000
|
a
|
b
|
|
5.1
|
|
Oxidizing liquids of packing group I
|
3000
|
a
|
b
|
|
Perchlorates, ammonium nitrate, ammonium nitrate fertilisers and ammonium nitrate emulsions or suspensions or gels
|
3000
|
3000
|
b
|
|
6.1
|
|
Toxic substances of packing group I
|
0
|
a
|
0
|
|
6.2
|
|
Infectious substances of Category A (UN Nos. 2814 and 2900, except for animal material)
|
a
|
0
|
0
|
|
8
|
|
Corrosive substances of packing group I
|
3000
|
a
|
b
|
a Not relevant.
b The provisions of 1.10.3 do not apply, whatever the quantity is.
c A value indicated in this column is applicable only if carriage in tanks is authorized, in accordance with Chapter
3.2, Table A, column (10) or (12). For substances that are not authorized for carriage in tanks, the instruction in
this column is not relevant.
d A value indicated in this column is applicable only if carriage in bulk is authorized, in accordance with Chapter
3.2, Table A, column (10) or (17). For substances that are not authorized for carriage in bulk, the instruction in
this column is not relevant.
For dangerous goods of Class 7, high consequence radioactive material is that with an activity equal to
or greater than a transport security threshold of 3 000 A2 per single package (see also 2.2.7.2.2.1)
except for the following radionuclides where the transport security threshold is given in Table
1.10.3.1.3 below.
Table 1.10.3.1.3: Transport security thresholds for specific radionuclides
|
Element
|
Radionuclide
|
Transport security threshold (TBq)
|
|
Americium
|
Am-241
|
0.6
|
|
Gold
|
Au-198
|
2
|
|
Cadmium
|
Cd-109
|
200
|
|
Californium
|
Cf-252
|
0.2
|
|
Curium
|
Cm-244
|
0.5
|
|
Cobalt
|
Co-57
|
7
|
|
Cobalt
|
Co-60
|
0.3
|
|
Caesium
|
Cs-137
|
1
|
|
Iron
|
Fe-55
|
8000
|
|
Germanium
|
Ge-68
|
7
|
|
Gadolinium
|
Gd-153
|
10
|
|
Iridium
|
Ir-192
|
0.8
|
|
Nickel
|
Ni-63
|
600
|
|
Palladium
|
Pd-103
|
900
|
|
Promethium
|
Pm-147
|
400
|
|
Polonium
|
Po-210
|
0.6
|
|
Plutonium
|
Pu-238
|
0.6
|
|
Plutonium
|
Pu-239
|
0.6
|
|
Radium
|
Ra-226
|
0.4
|
|
Ruthenium
|
Ru-106
|
3
|
|
Selenium
|
Se-75
|
2
|
|
Strontium
|
Sr-90
|
10
|
|
Thallium
|
Tl-204
|
200
|
|
Thulium
|
Tm-170
|
200
|
|
Ytterbium
|
Yb-169
|
3
|
For mixtures of radionuclides, determination of whether or not the transport security threshold has
been met or exceeded can be calculated by summing the ratios of activity present for each
radionuclide divided by the transport security threshold for that radionuclide. If the sum of the
fractions is less than 1, then the radioactivity threshold for the mixture has not been met nor exceeded.
This calculation can be made with the formula:
Where:
Ai = activity of radionuclide i that is present in a package (TBq)
Ti = transport security threshold for radionuclide i (TBq).
When radioactive material possesses subsidiary risks of other classes, the criteria of table 1.10.3.1.2
shall also be taken into account (see also 1.7.5).
Security plans
Carriers, consignors and other participants specified in 1.4.2 and 1.4.3 engaged in the carriage of high
consequence dangerous goods (see Table 1.10.3.1.2) or high consequence radioactive material (see
1.10.3.1.3) shall adopt, implement and comply with a security plan that addresses at least the elements
specified in 1.10.3.2.2.
The security plan shall comprise at least the following elements:
(a) Specific allocation of responsibilities for security to competent and qualified persons with
appropriate authority to carry out their responsibilities;
(b) Records of dangerous goods or types of dangerous goods concerned;
(c) Review of current operations and assessment of security risks, including any stops necessary to
the transport operation, the keeping of dangerous goods in the vehicle, tank or container before,
during and after the journey and the intermediate temporary storage of dangerous goods during
the course of intermodal transfer or transhipment between units as appropriate;
(d) Clear statement of measures that are to be taken to reduce security risks, commensurate with
the responsibilities and duties of the participant, including:
- training;
- security policies (e.g. response to higher threat conditions, new employee/employment
verification, etc.);
- operating practices (e.g. choice/use of routes where known, access to dangerous goods
in intermediate temporary storage (as defined in (c)), proximity to vulnerable
infrastructure etc.);
- equipment and resources that are to be used to reduce security risks;
(e) Effective and up to date procedures for reporting and dealing with security threats, breaches of
security or security incidents;
(f) Procedures for the evaluation and testing of security plans and procedures for periodic review
and update of the plans;
(g) Measures to ensure the physical security of transport information contained in the security
plan; and
(h) Measures to ensure that the distribution of information relating to the transport operation
contained in the security plan is limited to those who need to have it. Such measures shall not
preclude the provision of information required elsewhere in ADR.
NOTE: Carriers, consignors and consignees should co-operate with each other and with competent
authorities to exchange threat information, apply appropriate security measures and respond to
security incidents.
Devices, equipment or arrangements to prevent the theft of the vehicle carrying high consequence
dangerous goods (see Table 1.10.3.1.2) or high consequence radioactive material (see 1.10.3.1.3) and
its cargo, shall be applied and measures taken to ensure that these are operational and effective at all
times. The application of these protective measures shall not jeopardize emergency response.
NOTE: When appropriate and already fitted, the use of transport telemetry or other tracking
methods or devices should be used to monitor the movement of high consequence dangerous goods
(see Table 1.10.3.1.2) or high consequence radioactive material (see 1.10.3.1.3).
In accordance with the provisions of 1.1.3.6, the requirements of 1.10.1, 1.10.2, 1.10.3 and 8.1.2.1 (d)
do not apply when the quantities carried in packages on a transport unit do not exceed those referred
to in 1.1.3.6.3, except for UN Nos. 0029, 0030, 0059, 0065, 0073, 0104, 0237, 0255, 0267, 0288,
0289, 0290, 0360, 0361, 0364, 0365, 0366, 0439, 0440, 0441, 0455, 0456 and 0500 and except for
UN Nos. 2910 and 2911 if the activity level exceeds the A2 value (see first indent of 1.1.3.6.2). In
addition, the requirements of 1.10.1, 1.10.2, 1.10.3 and 8.1.2.1 (d) do not apply when the quantities
carried in tanks or in bulk on a transport unit do not exceed those referred to in 1.1.3.6.3. In addition
the provisions of this Chapter do not apply to the carriage of UN No. 2912 RADIOACTIVE
MATERIAL, LOW SPECIFIC ACTIVITY (LSA-I) and UN No. 2913 RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL,
SURFACE CONTAMINATED OBJECTS (SCO-I).
For radioactive material, the provisions of this Chapter are deemed to be complied with when the
provisions of the Convention on Physical Protection of Nuclear Material1 and the IAEA circular on
"The Physical Protection of Nuclear Material and Nuclear Facilities"2 are applied.
Classification
GENERAL PROVISIONS
Introduction
Previous Matter
Next Matter