Criteria
The heading of Class 6.1 covers substances of which it is known by experience or regarding which it
is presumed from experiments on animals that in relatively small quantities they are able by a single
action or by action of short duration to cause damage to human health, or death, by inhalation, by
cutaneous absorption or by ingestion.
NOTE: Genetically modified microorganisms and organisms shall be assigned to this Class if they
meet the conditions for this Class.
Substances of Class 6.1 are subdivided as follows:
T Toxic substances without subsidiary risk:
T1 Organic, liquid;
T2 Organic, solid;
T3 Organometallic substances;
T4 Inorganic, liquid;
T5 Inorganic, solid;
T6 Liquid, used as pesticides;
T7 Solid, used as pesticides;
T8 Samples;
T9 Other toxic substances;
TF Toxic substances, flammable:
TF1 Liquid;
TF2 Liquid, used as pesticides;
TF3 Solid;
TS Toxic substances, self-heating, solid;
TW Toxic substances, which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases:
TW1 Liquid;
TW2 Solid;
TO Toxic substances, oxidizing:
TO1 Liquid;
TO2 Solid;
TC Toxic substances, corrosive:
TC1 Organic, liquid;
TC2 Organic, solid;
TC3 Inorganic, liquid;
TC4 Inorganic, solid;
TFC Toxic substances, flammable, corrosive;
TFW Toxic substances, flammable, which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases.
Definitions
For the purposes of ADR:
LD50 (median lethal dose) for acute oral toxicity is the statistically derived single dose of a substance
that can be expected to cause death within 14 days in 50 per cent of young adult albino rats when
administered by the oral route. The LD50 value is expressed in terms of mass of test substance per
mass of test animal (mg/kg);
LD50 for acute dermal toxicity is that dose of the substance which, administered by continuous contact
for 24 hours with the bare skin of albino rabbits, is most likely to cause death within 14 days in one
half of the animals tested. The number of animals tested shall be sufficient to give a statistically
significant result and be in conformity with good pharmacological practice. The result is expressed in
milligrams per kg body mass;
LC50 for acute toxicity on inhalation is that concentration of vapour, mist or dust which, administered
by continuous inhalation to both male and female young adult albino rats for one hour, is most likely
to cause death within 14 days in one half of the animals tested. A solid substance shall be tested if at
least 10% (by mass) of its total mass is likely to be dust in a respirable range, e.g. the aerodynamic
diameter of that particle-fraction is 10 μm or less. A liquid substance shall be tested if a mist is likely
to be generated in a leakage of the transport containment. Both for solid and liquid substances more
than 90% (by mass) of a specimen prepared for inhalation toxicity shall be in the respirable range as
defined above. The result is expressed in milligrams per litre of air for dusts and mists or in millilitres
per cubic metre of air (parts per million) for vapours.
Classification and assignment of packing groups
Substances of Class 6.1 shall be classified in three packing groups according to the degree of danger
they present for carriage, as follows:
Packing group I: highly toxic substances
Packing group II: toxic substances
Packing group III: slightly toxic substances.
Substances, mixtures, solutions and articles classified in Class 6.1 are listed in Table A of Chapter 3.2.
The assignment of substances, mixtures and solutions not mentioned by name in Table A of Chapter
3.2 to the relevant entry of sub-section 2.2.61.3 and to the relevant packing group in accordance with
the provisions of Chapter 2.1, shall be made according to the following criteria in 2.2.61.1.6 to
2.2.61.1.11.
To assess the degree of toxicity, account shall be taken of human experience of instances of accidental
poisoning, as well as special properties possessed by any individual substances: liquid state, high
volatility, any special likelihood of cutaneous absorption, and special biological effects.
In the absence of observations on humans, the degree of toxicity shall be assessed using the available
data from animal experiments in accordance with the table below:
|
|
Packing group |
Oral toxicity LD50 (mg/kg) |
Dermal toxicity LD50 (mg/kg) |
Inhalation toxicity by dusts and mists LC50 (mg/l) |
|
Highly toxic |
I |
≤ 5 |
50 |
0.2 |
|
Toxic |
II |
> 5 and 50 |
> 50 and 200 |
> 0.2 and 2 |
|
Slightly toxic |
III a |
> 50 and 300 |
> 200 and 1 000 |
> 2 and 4 |
a Tear gas substances shall be included in packing group II even if data concerning their
toxicity correspond to packing group III criteria.
Where a substance exhibits different degrees of toxicity for two or more kinds of exposure, it shall be
classified under the highest such degree of toxicity.
Substances meeting the criteria of Class 8 and with an inhalation toxicity of dusts and mists (LC50)
leading to packing group I shall only be accepted for an allocation to Class 6.1 if the toxicity through
oral ingestion or dermal contact is at least in the range of packing groups I or II. Otherwise an
assignment to Class 8 shall be made if appropriate (see 2.2.8.1.5).
The criteria for inhalation toxicity of dusts and mists are based on LC50 data relating to 1-hour
exposure, and where such information is available it shall be used. However, where only LC50 data
relating to 4-hour exposure are available, such figures can be multiplied by four and the product
substituted in the above criteria, i.e. LC50 value multiplied by four (4 hour) is considered the
equivalent of LC50 (1 hour).
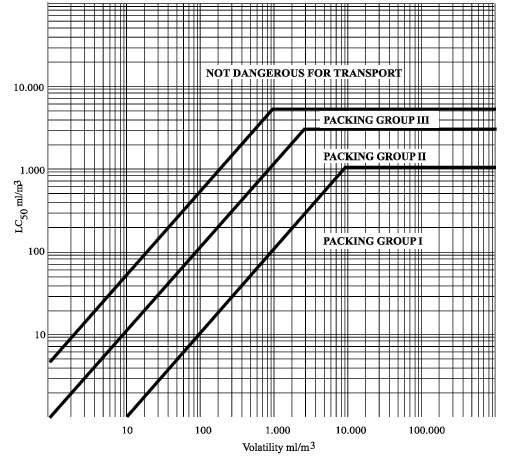
Inhalation toxicity of vapours
Liquids giving off toxic vapours shall be classified into the following groups where "V" is the
saturated vapour concentration (in ml/m3 of air) (volatility) at 20 °C and standard atmospheric
pressure:
|
Packing group |
||
|
Highly toxic |
I |
Where V ≥ 10 LC50 and LC50 ≤ 1 000 ml/m3 |
|
Toxic |
II |
Where V ≥ LC50 and LC50 ≤ 3 000 ml/m3 and the criteria for packing group I are not met |
|
Slightly toxic |
IIIa |
Where V ≥ 1/5 LC50 and LC50 ≤ 5 000 ml/m3 and the criteria for packing groups I and II are not met |
a Tear gas substances shall be included in packing group II even if data concerning their
toxicity correspond to packing group III criteria.
These criteria for inhalation toxicity of vapours are based on LC50 data relating to 1-hour exposure,
and where such information is available, it shall be used.
However, where only LC50 data relating to 4-hour exposure to the vapours are available, such figures
can be multiplied by two and the product substituted in the above criteria, i.e. LC50 (4 hour) × 2 is
considered the equivalent of LC50 (1 hour).
In this figure, the criteria are expressed in graphical form, as an aid to easy classification. However,
due to approximations inherent in the use of graphs, substances falling on or near group borderlines
shall be checked using numerical criteria.
GROUP BORDERLINES INHALATION TOXICITY OF VAPOURS
Mixtures of liquids
Mixtures of liquids which are toxic on inhalation shall be assigned to packing groups according to the
following criteria:
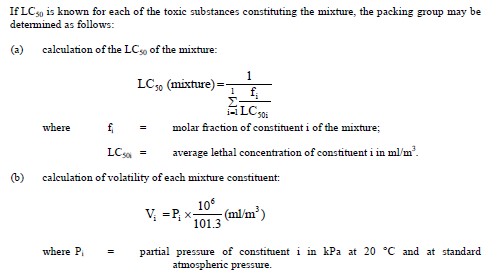
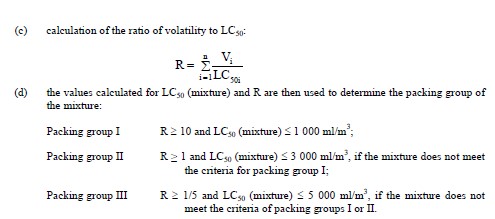
In the absence of LC50 data on the toxic constituent substances, the mixture may be assigned to a
group based on the following simplified threshold toxicity tests. When these threshold tests are used,
the most restrictive group shall be determined and used for carrying the mixture.
