mixtures with highly toxic ingredients
acute 1 or chronic 1 ingredients with acute toxicities well below 1 mg/l and/or chronic toxicities
well below 0.1 mg/l (if non-rapidly degradable) and 0.01 mg/l (if rapidly degradable) may
influence the toxicity of the mixture and are given increased weight in applying the summation
method. when a mixture contains ingredients classified as acute or chronic 1, the tiered approach
described in 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.2 and 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.3 shall be applied using a weighted sum by
multiplying the concentrations of acute 1 and chronic 1 ingredients by a factor, instead of merely
adding up the percentages. this means that the concentration of "acute 1" in the left column of
table 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.2.2 and the concentration of "chronic 1" in the left column of table
2.2.9.1.10.4.6.3.3 are multiplied by the appropriate multiplying factor. the multiplying factors to
be applied to these ingredients are defined using the toxicity value, as summarised in
table 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.4 below. therefore, in order to classify a mixture containing acute 1 and/or
chronic 1 ingredients, the classifier needs to be informed of the value of the m factor in order to
apply the summation method. alternatively, the additivity formula (see 2.2.9.1.10.4.5.2) may be
used when toxicity data are available for all highly toxic ingredients in the mixture and there is
convincing evidence that all other ingredients, including those for which specific acute and/or
chronic toxicity data are not available, are of low or no toxicity and do not significantly contribute
to the environmental hazard of the mixture.
table 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.4: multiplying factors for highly toxic ingredients of mixtures
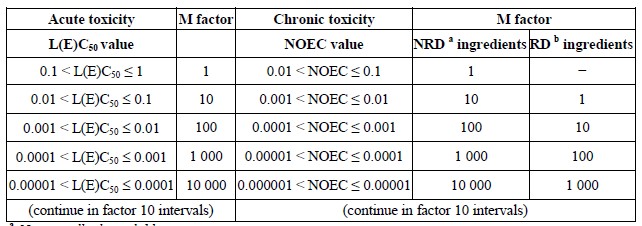
a non-rapidly degradable.
b rapidly degradable.
