substances shall be classified as "environmentally hazardous substances (aquatic environment)", if
they satisfy the criteria for acute 1, chronic 1 or chronic 2, according to table 2.2.9.1.10.3.1. these
criteria describe in detail the classification categories. they are diagrammatically summarized in
table 2.2.9.1.10.3.2.
11 special guidance on data interpretation is provided in chapter 4.1 and annex 9 of the ghs.
12 see chapter 4.1 and annex 9, paragraph a9.4.2.2.3 of the ghs.
table 2.2.9.1.10.3.1: categories for substances hazardous to the aquatic environment (see note 1)
(a) acute (short-term) aquatic hazard
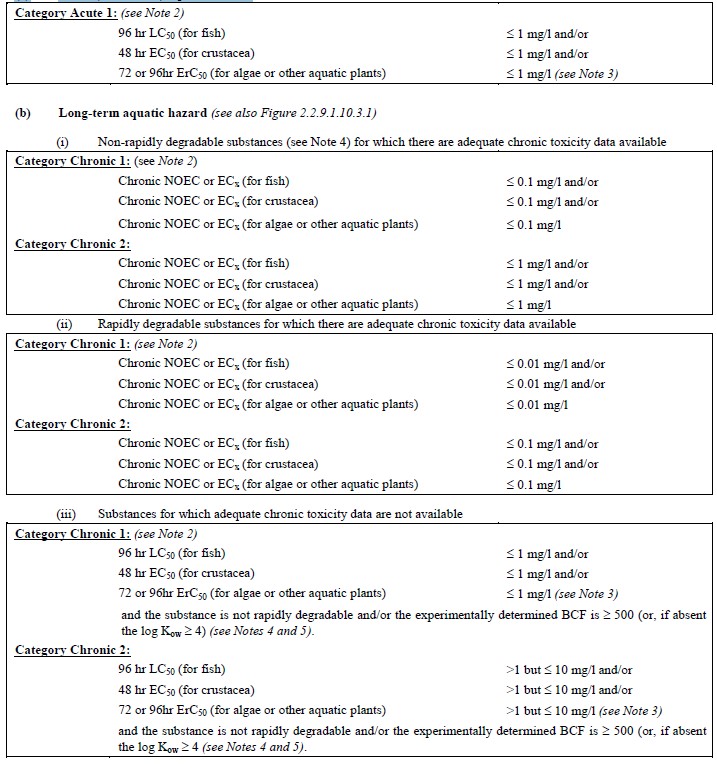
note 1: the organisms fish, crustacea and algae are tested as surrogate species covering a range of
trophic levels and taxa, and the test methods are highly standardized. data on other organisms may
also be considered, however, provided they represent equivalent species and test endpoints.
note 2: when classifying substances as acute 1 and/or chronic 1 it is necessary at the same time to
indicate an appropriate m factor (see 2.2.9.1.10.4.6.4 ) to apply the summation method.
note 3: where the algal toxicity erc50 (= ec50 (growth rate)) falls more than 100 times below the
next most sensitive species and results in a classification based solely on this effect, consideration
shall be given to whether this toxicity is representative of the toxicity to aquatic plants. where it can
be shown that this is not the case, professional judgment shall be used in deciding if classification
shall be applied. classification shall be based on the erc50. in circumstances where the basis of the
ec50 is not specified and no erc50 is recorded, classification shall be based on the lowest ec50
available.
note 4: lack of rapid degradability is based on either a lack of ready biodegradability or other
evidence of lack of rapid degradation. when no useful data on degradability are available, either
experimentally determined or estimated data, the substance shall be regarded as not rapidly
degradable.
note 5: potential to bioaccumulate, based on an experimentally derived bcf ≥ 500 or, if absent,
a log kow ≥ 4 provided log kow is an appropriate descriptor for the bioaccumulation potential of the
substance. measured log kow values take precedence over estimated values and measured bcf values
take precedence over log kow values.
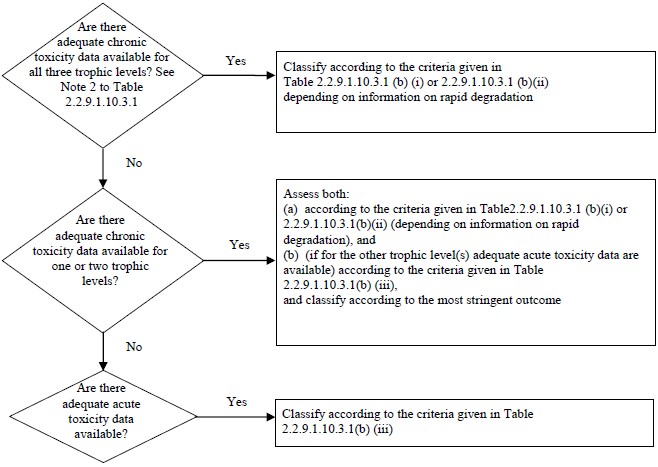
figure 2.2.9.1.10.3.1: categories for substances long-term hazardous to the aquatic environment